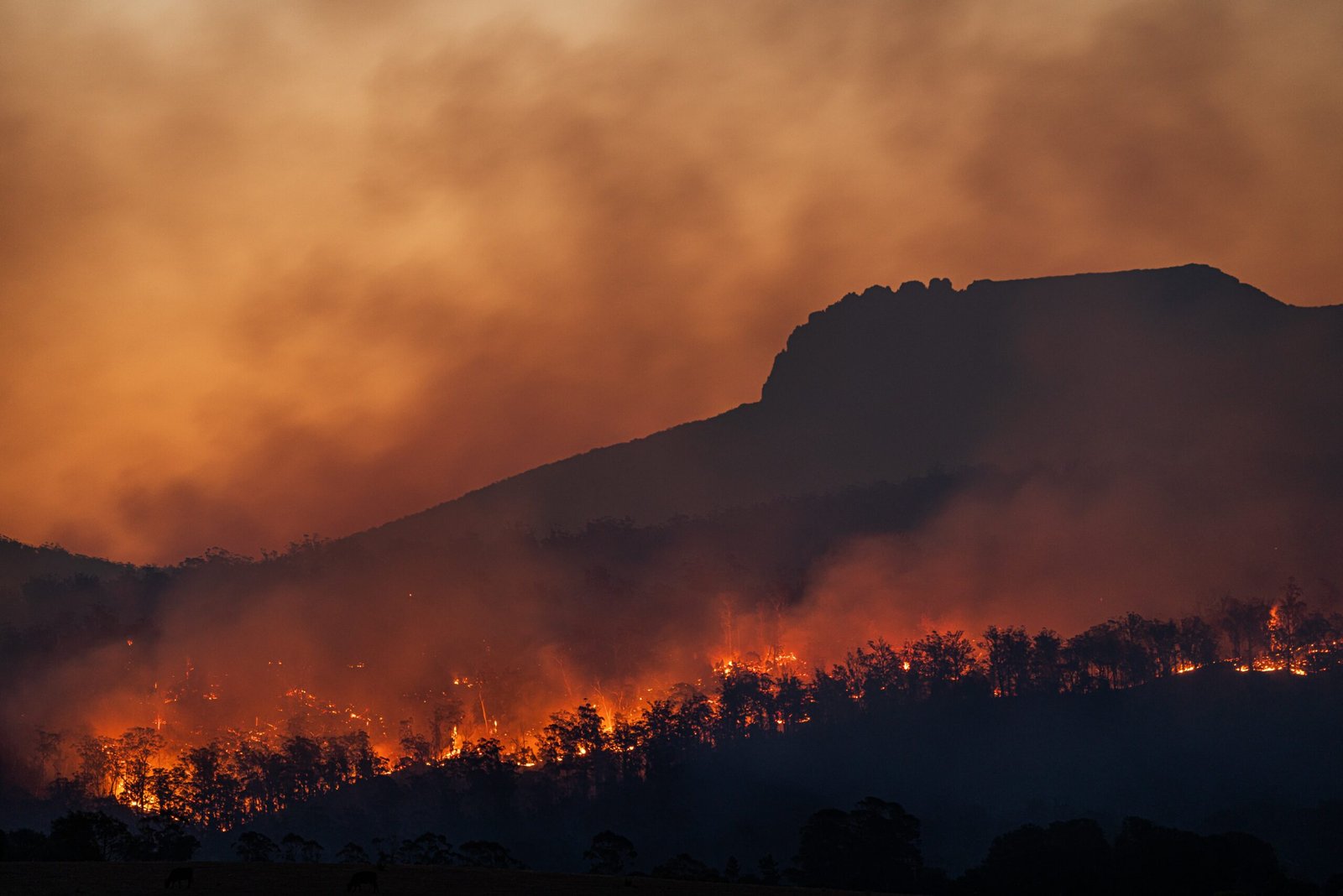
Climate change is not only affecting our environment but also posing a significant threat to global food security. The changing climate patterns, including rising temperatures, more frequent extreme weather events, and shifting rainfall patterns, are disrupting agricultural systems worldwide.
One of the major concerns is the impact of climate change on crop production. Rising temperatures and prolonged heatwaves can negatively affect crop yields and reduce the availability of arable land. Additionally, changes in rainfall patterns can lead to droughts or floods, further damaging crops and causing food shortages.
Climate change also affects the distribution and availability of water resources, which are vital for agriculture. As temperatures increase, evaporation rates rise, leading to water scarcity in many regions. This scarcity can limit irrigation capabilities, making it difficult for farmers to grow crops successfully.
Moreover, the changing climate is contributing to the spread of pests and diseases, affecting both crops and livestock. Warmer temperatures can create more favorable conditions for pests, leading to increased infestations and crop damage. This can result in lower crop yields and decreased food production.
The impact of climate change on global food security goes beyond crop production. It also affects livestock production and fisheries. Changing climate conditions can disrupt grazing patterns, reduce the availability of pastureland, and increase the risk of diseases among livestock. In the case of fisheries, rising sea temperatures and ocean acidification can impact fish populations, affecting the livelihoods of millions who depend on fishing for their food and income.
To address the challenges posed by climate change to global food security, there is a need for adaptation and mitigation strategies. This includes investing in climate-resilient agricultural practices, improving water management systems, promoting sustainable farming techniques, and supporting small-scale farmers. Additionally, international cooperation and policy interventions are crucial to ensure food security for all, especially in vulnerable regions.
In conclusion, climate change is jeopardizing global food security by disrupting agricultural systems, reducing crop yields, affecting water resources, and increasing the spread of pests and diseases. Urgent action is required to mitigate the impact of climate change on food production and ensure a sustainable and secure food future for all.